Did you know the body pain and fatigue that you suffer from every day after work might be due to incorrect practices at work? Most office jobs involve using computers today, which means the workers are usually seated in their office chairs throughout the day. And not many people are aware of the correct and incorrect posture, and they don’t realize that they’re sitting in an incorrect posture for several hours every day!
Most workplaces feature standard and generalized office design, with little to no attention to ergonomics. Employers don’t realize the fact that a generalized office design won’t suit the comfort needs of all employees. Every employee’s body proportion is different, and each employee would need office equipment and tools that enable them to work comfortably.
You can’t even come to imagine the consequences of poor workplace ergonomics. From problems as small as back and shoulder pain to ailments as serious as Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs), poor ergonomics can have grave consequences that can last a lifetime if not addressed in time.
You’ve got to sit in the correct posture to ensure that you aren’t at the risk of falling sick. This blog post will help you understand what the correct posture is and how you can ensure proper ergonomics at your workstation.
The Neutral Posture
The neutral posture is the one that ensures minimal to no stress on any part of your body. When you’re sitting or standing in an incorrect posture, there’s excessive stress in your lower back and on the body’s soft tissues. This stress becomes the basis of MSDs and other chronic posture-related health problems.
However, all possible risks associated with awkward postures are mitigated when you’re in a neutral posture. Let’s see how you can maintain a neutral posture at work.
While Sitting
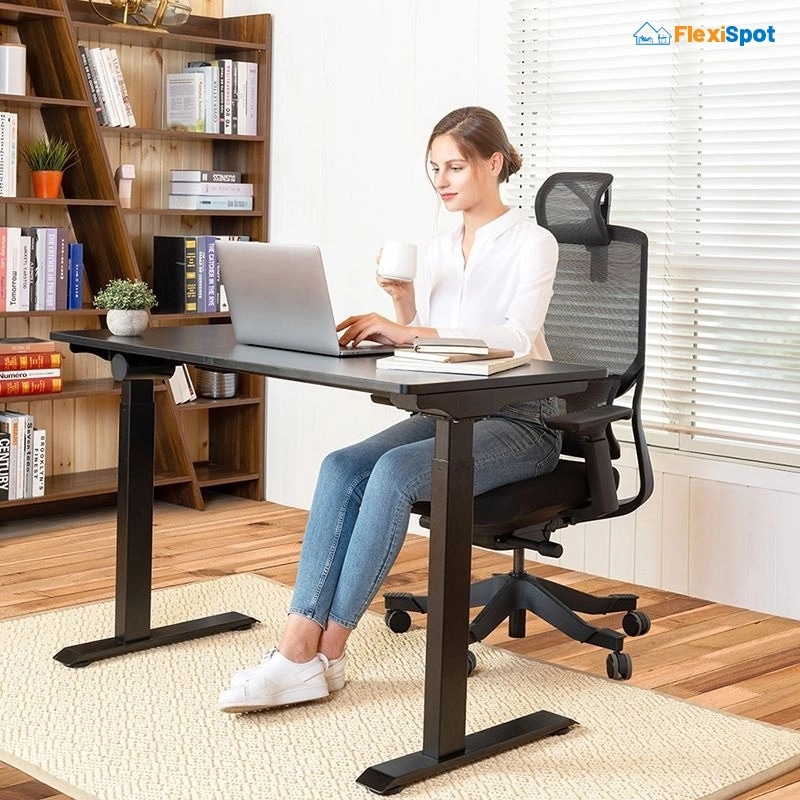
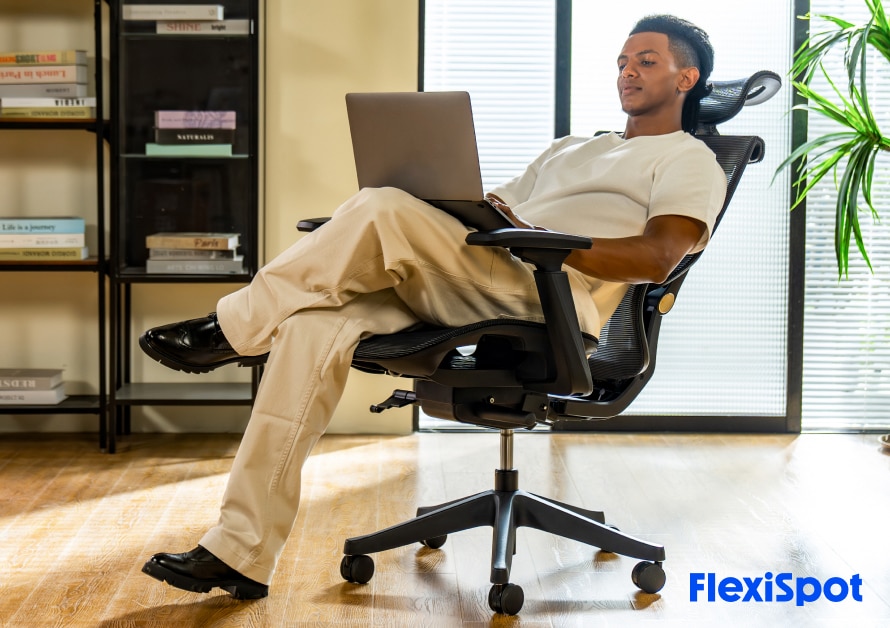
Like most office jobs, if your job requires you to sit in front of your computer screen for extended hours, you’re at a high risk of developing MSDs. You’ve got to be even more conscious about your posture. If the posture you’re currently working in tires you out, it’s a sign that it’s not how you must be sitting.
Sit in a way that you aren’t leaning forward or aren’t slumped in your office chair. Your back must be comfortably resting on the backrest that’s adjusted to your back’s curvature. Your feet should be placed flat on the floor. You must be fully on your seat (not on the edge of the seat to reach the desk), with your thighs supported by the seat. Your elbows must be resting on the armrests, and your wrists should sit comfortably on the keyboard.
While Standing
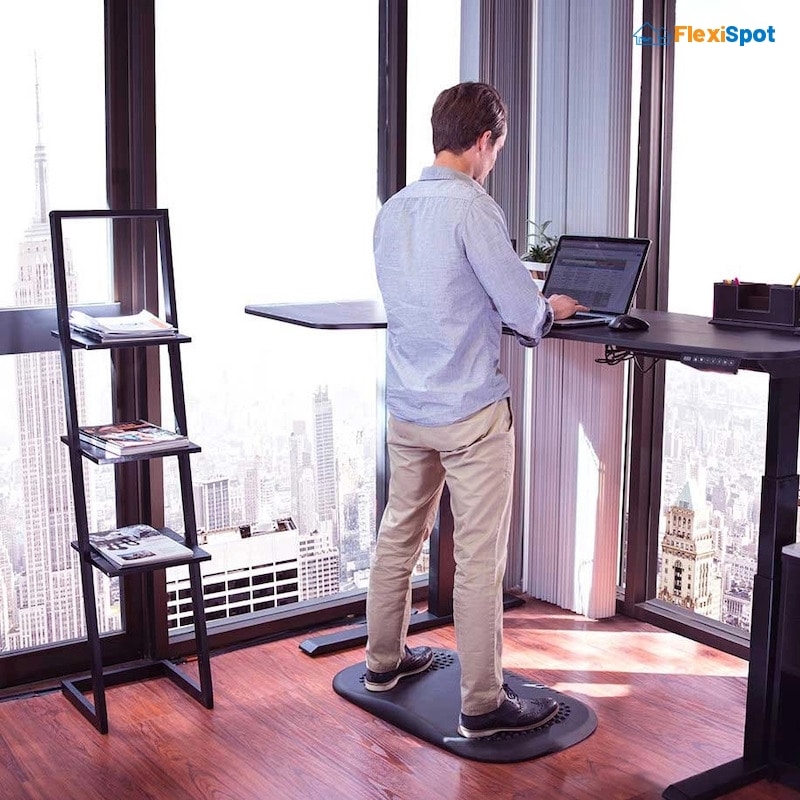
If your job requires you to stand all day long or your employer has been considerate enough to arrange ergonomic workstations like the Willow Solid Wood Standing Desk for you, you should make sure that you’re standing correctly. You read that right; there’s a right and wrong way to stand too.
Make sure you’re standing on a flat surface with your feet entirely flat on the floor. Your best bet is to invest in anti-fatigue mats and wear shoes that have insoles to reduce the stress and fatigue to the muscles of your legs. Don’t bend your knees. Try to keep them locked straight. You should stand such that your upper arms are at your sides, with your elbows bent at an angle of 90 to 100 degrees. The wrists should rest on the desk straight and shouldn’t be pressed into the edge of the desk or the keyboard. And your head must not be tilted. It should be centered between your shoulders.
If you maintain a neutral posture at work, the risk of MSDs and other posture-related health problems can be greatly reduced.
Photo Credit: Core Balance Movement
What are Ergonomic Work Zones
You can only maintain a neutral posture if your work desk is organized and arranged according to the ergonomic work zones. All your work tools must be arranged correctly to make your work desk ergonomic. The placement of your work tools has a significant impact on your posture. For example, you’ll have no option but to bend forward to reach your placed too far keyboard.
For this reason, there’s a work zone model in place that can help you arrange your work desk ergonomically. There are 3 work zones, and each work zone requires a different extent of motion to perform an action within that zone.
Let’s look at the 3 working zones and understand how you can ensure you’re working in ergonomic conditions.
Primary Work Zone
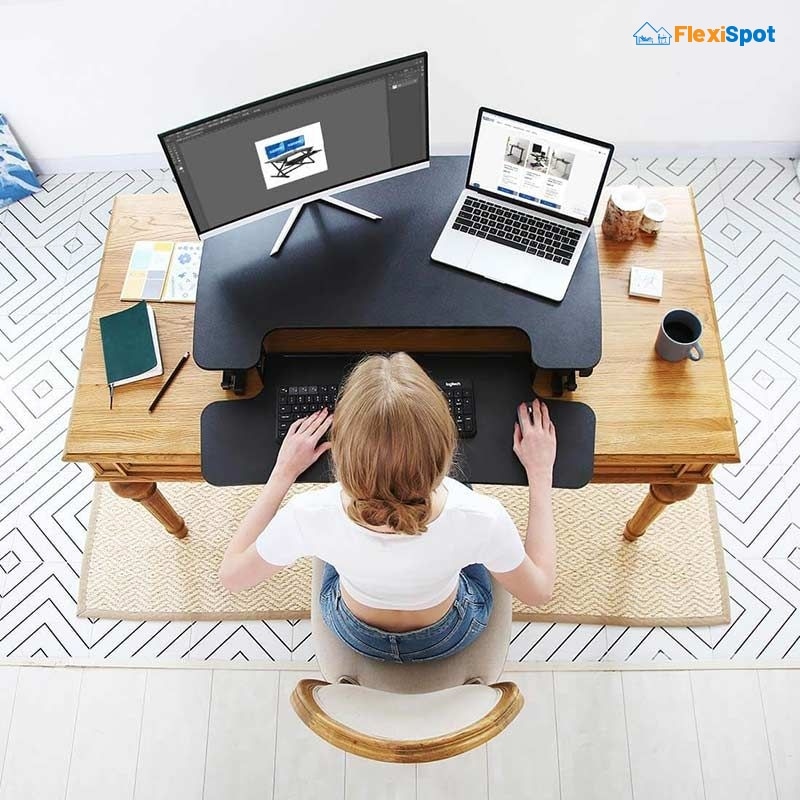
Zone 1, or the primary work zone, is the area of your work desk that’s in your immediate reach. It should be about 30to 40cm away from the neutral sitting posture. It’s the zone that you’re able to reach while being seated in a neutral posture. This means everything that you’ll be using most frequently throughout the day must be placed in this zone.
Your laptop, keyboard, mouse, notepad, and pen must be placed in the primary working zone so that you don’t have to extend or stretch your body every time you’ve got to use essential work tools.
With the tools and equipment you need most frequently placed in the primary zone, you don’t have to move your upper arms at all, which significantly reduces the stress on your upper body and thereby mitigates the risk of MSDs.
Secondary Work Zone
Zone 2 is the working zone where you’ll arrange everything that you need less often than the items placed in the primary zone. It should be approximately at a distance that’s equal to an arm’s length. You must place things like reference material, files, water bottles, or mugs in the horizontal secondary zone that you can reach out with an extended arm.
Vertically, the secondary zone is the area that is at the height of 8 to 12 inches above your shoulder. You can place folders and reference books in this zone.
Non-Working or Reference Work Zone
The last working zone is Zone 3, which is also referred to as the reference zone or non-working zone. It’s the area that’s about 40 to 70cm away from your neutral position. This zone should be reserved for items that you rarely use during work.
Since this zone is further away, you’ll have to bend at the waist and extend your arm fully to reach it. If you place anything that you frequently need during work in zone 3, you’re putting yourself at the risk of MSDs and RSI by exposing yourself to repetitive movements that aren’t healthy for you.
You should use this zone to arrange accessories only like plants, photo frames, or any personal belongings you won’t need during the day.
Sometimes, there’s also a zone 4, but that’s not always the case. It’s only for workplaces where there’s plenty of documentation. Zone 4 is specifically reserved for storage cabinets, and to reach this zone, you’ll have to get up from your work desk and walk.
Why Use Ergonomic Work Zones
Now that you know what ergonomic working zones are, you may wonder why to use ergonomic working zones when you can arrange all your office tools and belongings on your work desk as per your liking. Well, you sure can do that, but we don’t recommend that. There are numerous reasons why you should use ergonomic work zones.
Helps You Maintain Correct Posture
The first and most important reason you should use ergonomic work zones is that they help you maintain the correct posture. If the things you use frequently are placed farther away, like your keyboard, you’ll be hunched forward in your seat all day long. But if the keyboard is placed in the primary work zone, you’ll be able to work while being seated in a neutral (read: correct) posture.
Similarly, if you keep your notepad further away in the secondary zone, you’ll have to stretch your arm and bend your back every time you’ll need it (which will be quite often if your job requires you to take frequent notes).
By following the work zone model, you can ensure that you’re maintaining the correct posture for most of the day!
Keeps Your Work Desk Neatly Organized
You can have everything that you need and all that you don’t need scattered all over your work desk, or you can arrange it all on the basis of the work zone model. Do we really need to tell you what’s better? Having everything arranged on your desk according to the work zone model won’t only keep your workstation looking neat and tidy, but it’ll also have a positive psychological impact.
Messy work desks tend to stress you out, whereas a neatly organized work desk has been found to reduce stress levels.
Enhances Productivity
Imagine receiving a call from your supervisor asking for a file that they need urgently in their office and not being able to find it. Would that stress you out? Of course, it would! If your desk is not organized properly, you’re bound to lose things in the mess.
This would increase your stress levels, and you just can’t work well under stress. If you keep everything organized according to the ergonomic work zones, you’ll see how smooth your work is. You’ll be able to work with greater focus and will be able to deliver higher quality work.
The ergonomic working zone model might just be what you need to ensure a healthy body and mind. If your workstation is a mess, take a break from work and start arranging things into working zones. You’ll feel better almost instantly. We promise!